In Vitro Fertilisation In Natural Cycle
What is it?
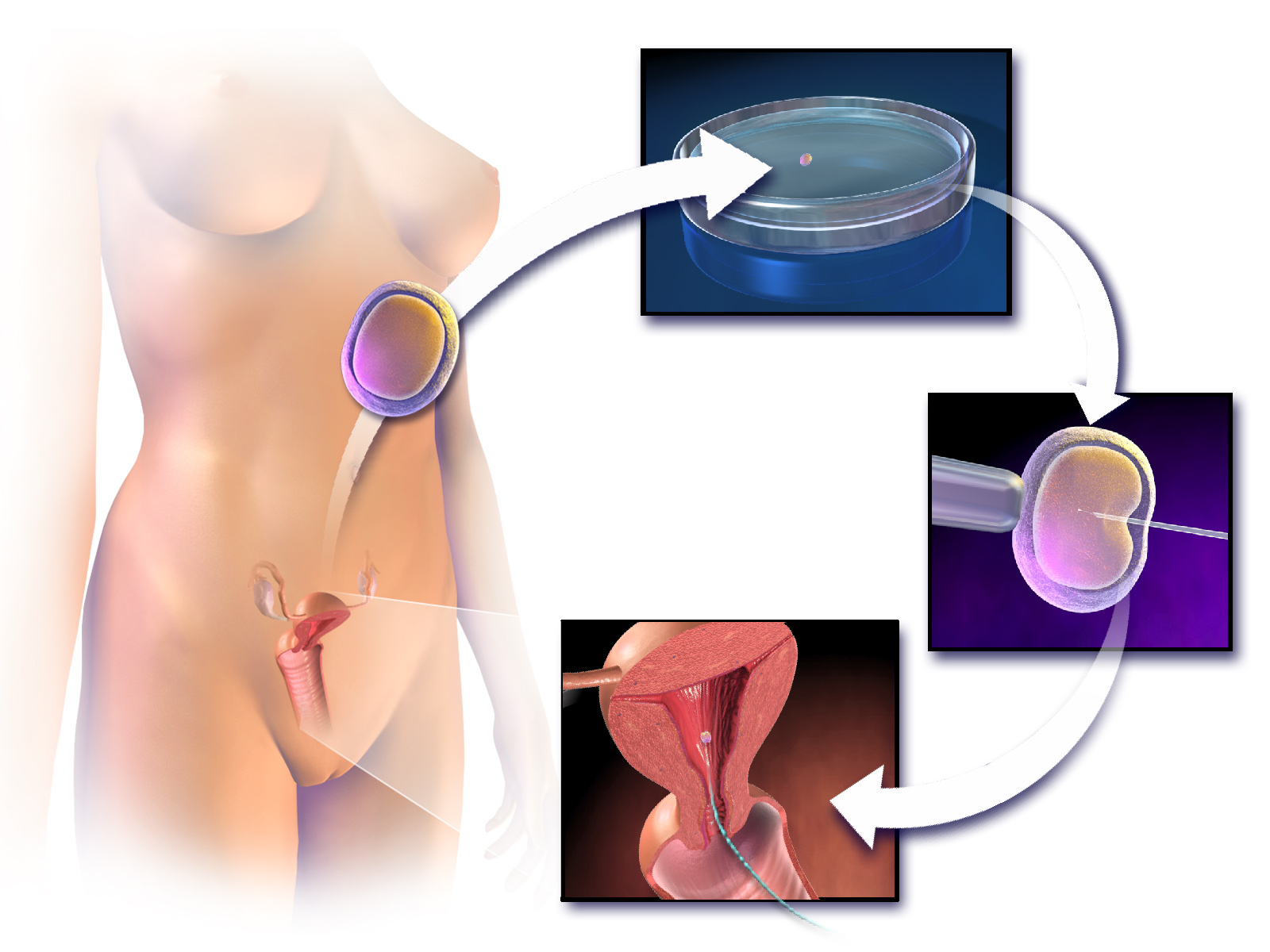
In vitro fertilisation in natural cycle is suitable for women who do not wish or are not able (for various reasons) to undergo a pharmaceutical ovarian stimulation. Woman undergoes ultrasound and hormonal – blood tests and as soon as the ovarian follicle has developed satisfactorily (> 18-20 mm), the mature ovum is collected from it. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) in the ovum is the next step from the partner’s sperm. In case of successful fertilisation, the embryo is kept in the laboratory and then transfered in the maternal uterus.
To who is it applied this method?
Theoretically this method may be applied to all women. However, it is ideal for women who have in the past undergone continuous and unsuccessful attempts of in vitro fertilisation despite the high dosages of gonadotropins.
What are the advantages of in vitro fertilisation in natural cycle?
The most important advantage of in vitro fertilisation in natural cycle is that the woman receives no hormones for the ovarian stimulation. They only medication received are the late-night HCG injections 34-36 hours before the collection of the ovum from the follicle. Moreover, there are very few chances of twin pregnancy and all the risks they can cause. Among the advantages is the psychological boost of the mother-to-be, who knows that she will have a child in a more “natural” way.
Are there any disadvantages?
The main disadvantage of this treatment is the presence of one and only follicle from which the ovum may be taken. This ovum must be appropriately mature in order to be fertilised, divided and then reproduce a healthy embryo, which will be transfered in the woman’s uterus.
What are the success rates of in vitro fertilisation in natural cycle?
For a woman who follows this treatment the success rates are between 8-12%. Rates may be lower in comparison to IVF however natural cycle is the appropriate choice for women who do not correspond positively to ovarian stimulation with medication.





